Interest on Illinois’ pension debt is $9.1B per year
A golden rule of finance is this: Debt that can’t be paid won’t be paid.
Illinois isn’t covering the interest payments on its pension debt. Those interest payments total $9.1 billion a year.
This is the reason Illinois’ pension debt continues to grow. As with personal credit card debt, until the interest is paid off none of the actual debt gets erased. Illinois’ pension debt is so large that it’s unlikely payments will cover the interest on the pension debt until 2028, according to a November 2016 special pension briefing from the Commission on Government Forecasting and Accountability.
Illinois politicians have known for years about the state’s pension crisis, even if they have not taken serious steps to address the problem. Gov. Bruce Rauner recently spoke out on the cost of interest on the pension debt. Former Gov. George Ryan weighed in as well, saying:
“First off, the biggest problem we got with the budget right now is the interest they are paying on the debt. If I were the governor, … I’d say we are never going to be able to pay the full debt back, so let’s eliminate half the debt right now and write it off.
“If that’s not constitutional, it might be worth changing the constitution. That would dramatically reduce the amount of interest that they’re paying. The bond ratings would go up and the interest would go down.”
Ryan seemed to be referring to the annual “interest cost” on Illinois’ pension debt, which is about $9.1 billion per year, or $25 million per day. The portion of interest cost that isn’t covered each year is simply added to the debt.
Why Illinois’ pension debt keeps growing
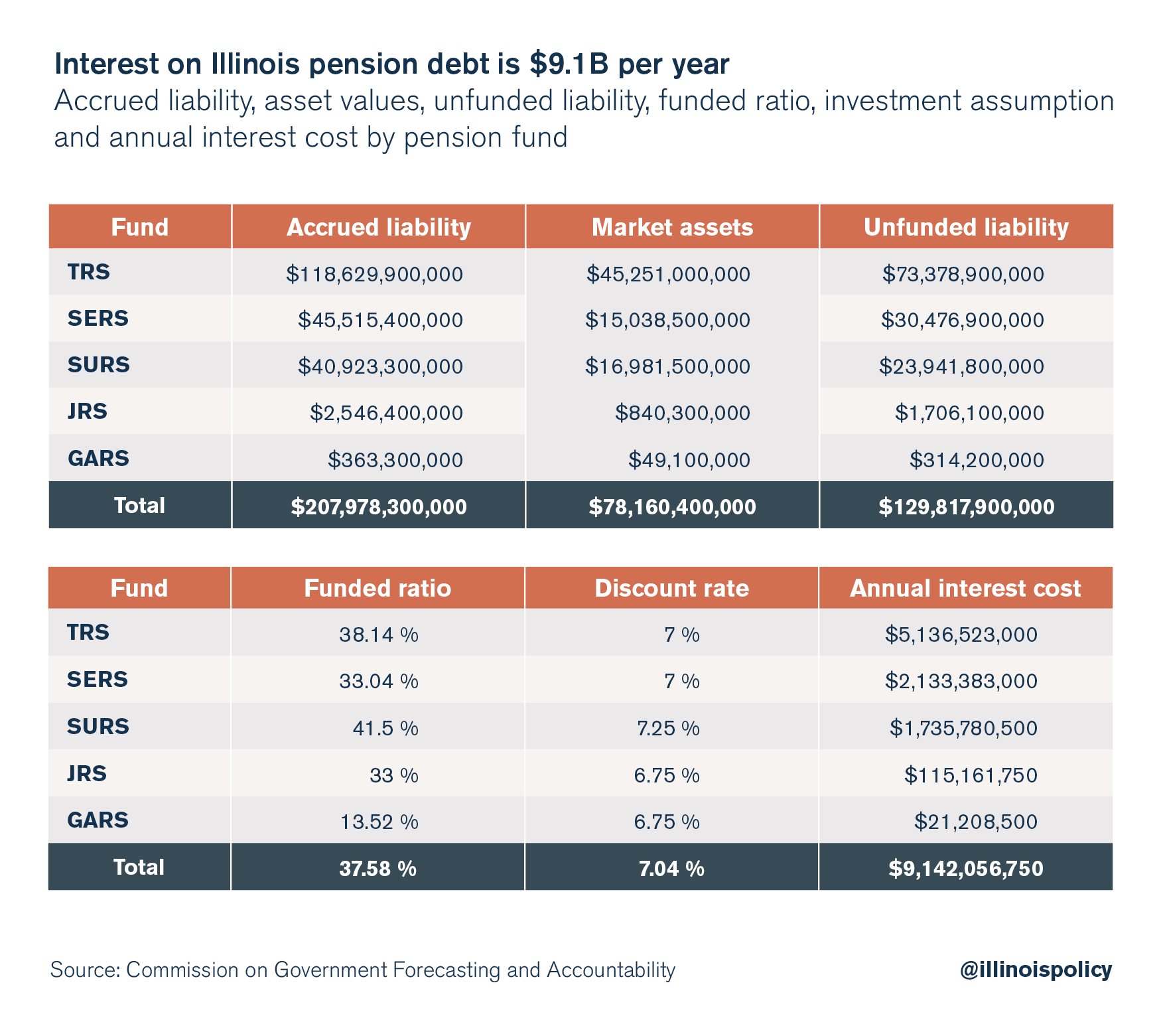
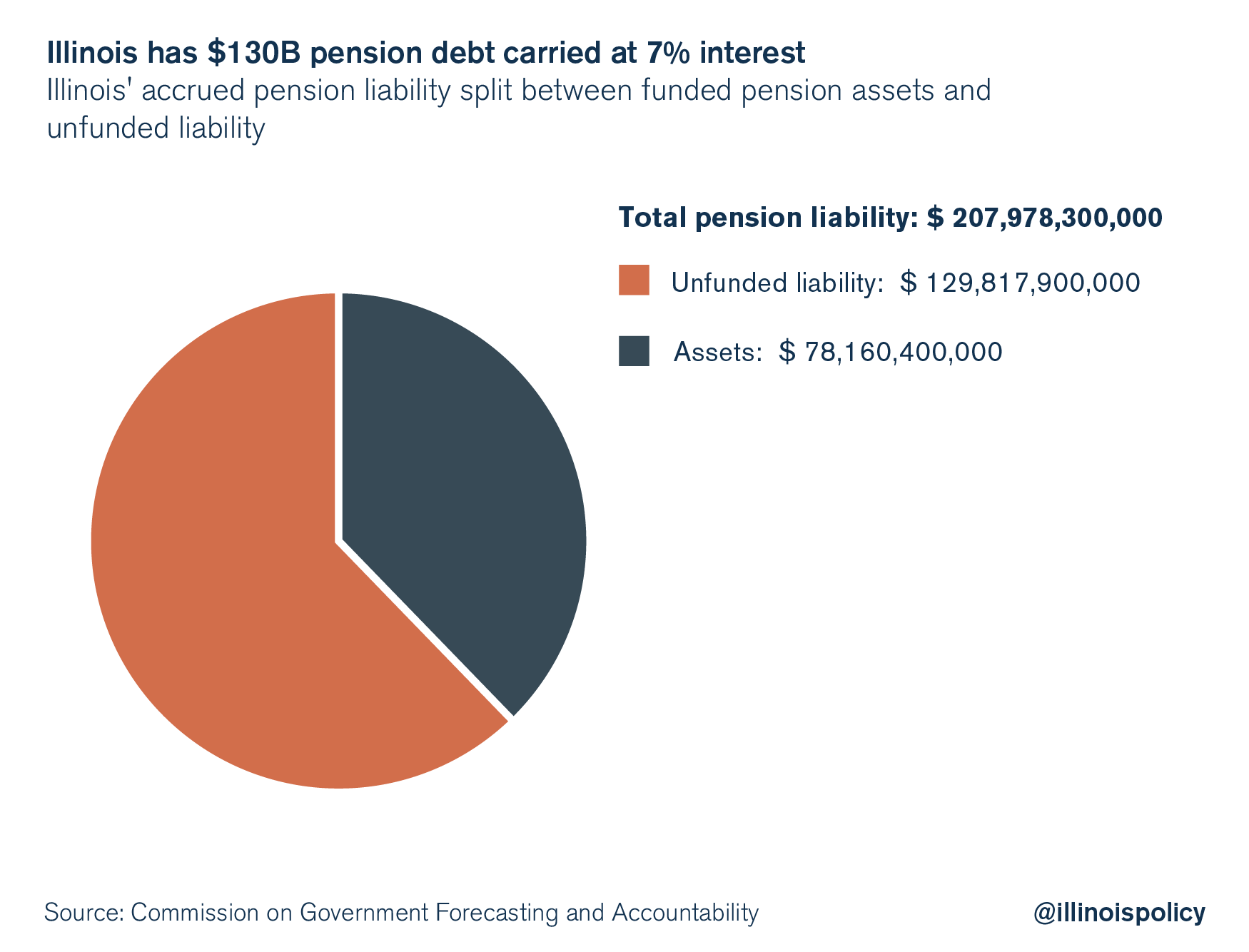
Illinois has about $78 billion in assets on hand to pay for pensions. But the present value of the state’s accrued liability is $208 billion. That leaves a difference of $130 billion, which is money the state owes – but doesn’t have.
Illinois pension math assumes an annual investment return rate of just over 7 percent on $208 billion in pension assets. If pension assets end up returning less than 7 percent per year, then the actual pension liability will end up being much larger than is currently assumed.
However, $130 billion of that accrued pension liability doesn’t exist, which is considered the pension debt. This debt does not bear interest like a bond does – but it functions the same way in reality. Because $130 billion is missing, Illinois will automatically miss out on the 7 percent annual investment return on that nonexistent $130 billion. This “missed” investment return is about $9.1 billion per year, and is essentially the interest cost on the $130 billion pension debt.
Illinois’ type of payment plan, which fails to cover interest, is called “negative amortization.” The debt principal continues to grow because the pension payment does not cover the interest cost. The portion of the interest payment that isn’t covered is added to the debt.
As actuary Tia Goss Sawhney explained, a full pension payment is made up of three parts:
Full payment = Employer normal cost + interest cost + principal reduction payment
However, Illinois’ scheduled pension payments are too small to cover the normal cost and interest cost, causing the unfunded liability to go up. For example, in fiscal year 2018, Illinois will make an $8.9 billion pension payment, which will cover the $2.1 billion employer normal cost and $6.8 billion of annual interest cost. However, the annual interest cost is actually $9.1 billion, meaning that after the employer’s portion of the normal cost, Illinois will come up $2.3 billion short on the interest payment. The unpaid portion of the interest cost is added to the debt, just as if a person didn’t cover the full interest payment on a home loan or credit card. In Illinois’ case, that $2.3 billion shortfall will be added to the pension debt.
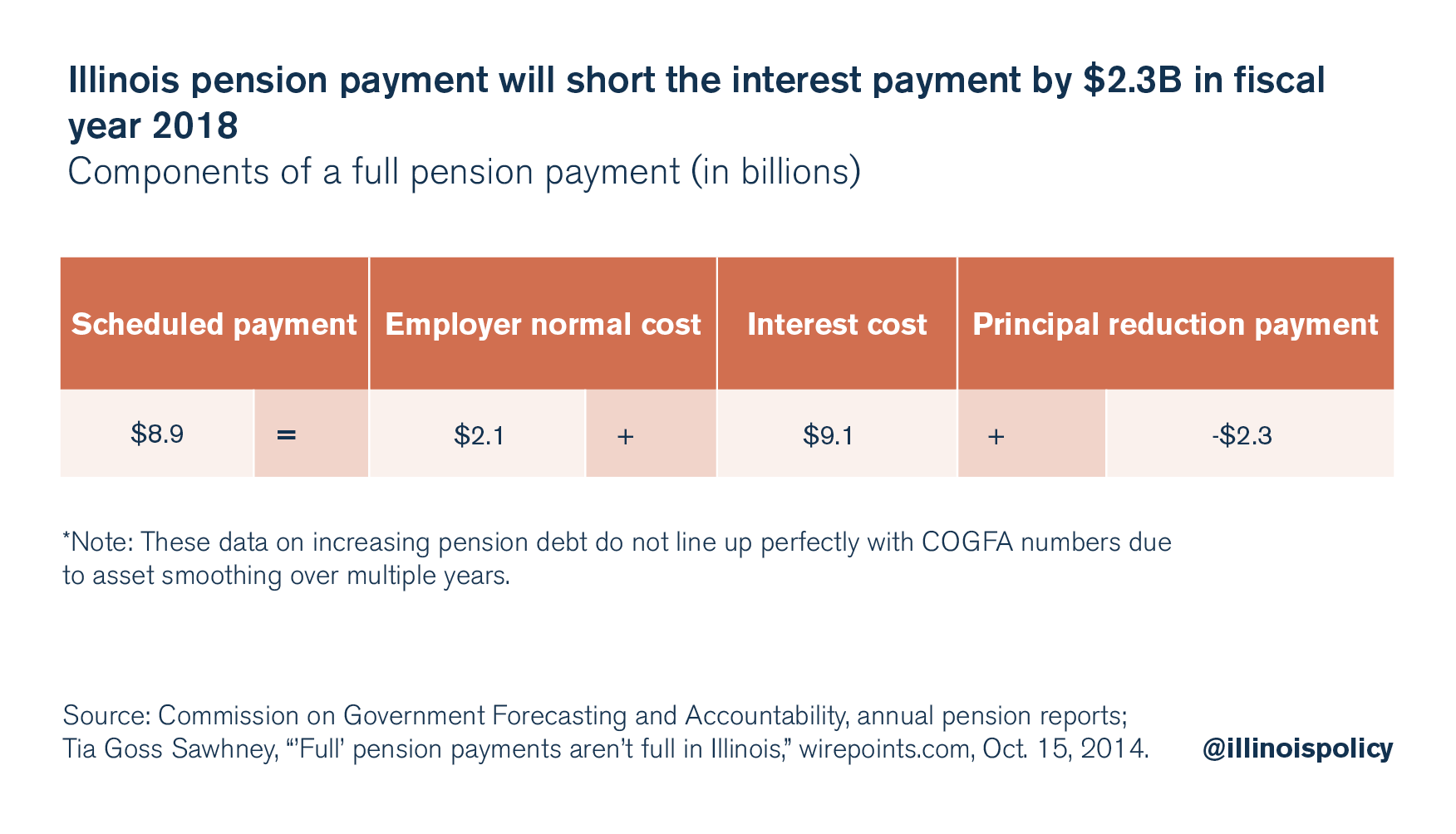
The reason the principal reduction payment is negative is because the debt grows.
Illinois needs a constitutional amendment to allow for real pension reform
As Ryan pointed out, Illinois’ pension math might never add up without reducing the $130 billion pension debt, which the Illinois Constitution currently protects from being restructured. Even though Illinois is already overtaxed, and pension costs are driving up taxes more each year, the state still can’t cover the interest cost on the pension debt until 2028. On top of that, many local communities like Chicago have pension problems that are even more severe than the state’s problems. And the math gets even worse if Illinois doesn’t hit investment returns of 7 percent per year.
A golden rule of finance is this: Debt that can’t be paid won’t be paid. The state should develop a contingency plan to repeal the Illinois Constitution’s pension protection clause and restructure pension obligations to pull Illinois out of a potential death spiral should the need arise. Such a plan should preserve benefits for government workers with modest pensions while means-testing the richer pension benefits. This would almost certainly be challenged as a violation of the contracts clause of the U.S. Constitution, and the U.S. Supreme Court might ultimately decide the matter.
Illinois might be one serious recession away from a financial death spiral. A deep recession would reduce the value of pension assets while also causing tax revenues to decline. Illinois’ pension obligations would increase just as tax revenues dried up. After such a recession ended, out-migration would likely surge as Illinoisans increasingly realized the impossibility of financing their government’s spending promises. If financial assets fall and do not recover, Illinois’ pension math might be doomed.
The battered ship of Illinois’ finances is lurching toward a rocky shore. Lawmakers should develop a contingency plan for an emergency situation, and be prepared to enact it in order to salvage the state’s finances.
